Connecting Controller (Master) to Third-Party Device (Slave)
The basic procedure largely corresponds to the description in Connecting Controller (Master) to Fieldbus Coupler (Slave). The main difference consists in making the third-party device known by adding and configuring a generic Modbus slave.
Place Devices on the Communication View
- Select a controller from the product catalog and use the mouse to drag it into the Network view (communication view).
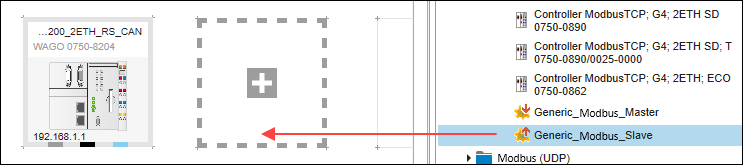
- Third-party devices are represented in e!COCKPIT by generic devices. These are also available in the product catalog:
In the “Other Communication Subscribers” folder of the product catalog, select the generic Modbus slave (“Generic_Modbus_Slave”) under “Modbus TCP” or “Modbus UDP” and drag it into the Network view as well.
Configure I/O Modules Used in the Device Detail View
Note: The Device Detail view is not available for third-party devices.
- Open the Device Detail view (in either graphical and tabular view) by double-clicking the controller.
- Arrange the I/O modules used analogously to your hardware by dragging them from the product catalog and positioning them after the device.
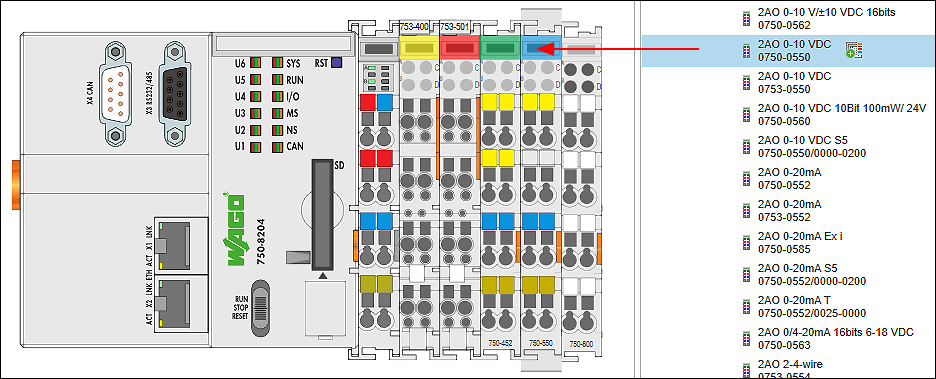
- Parameterize the I/O modules as needed by selecting them and making changes on the “Settings” panel for each.
- Go back to the Network view.
Connect Devices
- Click the gray connector (ETHERNET/Modbus) for one of the devices in the Network view (communication view) and hold down the mouse button.
- To connect the devices to each other, drag the connection line to the same type connector on the second device. Release the mouse button as soon as a green plus sign appears.
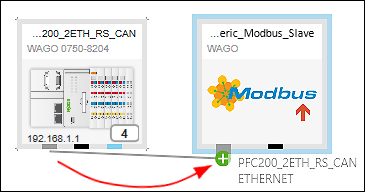
- The devices are connected. The arrow of the connection line indicates the automatically assigned roles of the device: The connection line starts at the master and ends at the slave.
Set the Protocol for the Connection
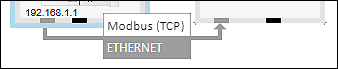
- To set the protocol for the connection, click the [Protocol] button in the context menu of the Modbus connector or connection.
- Select the desired connection (in this example: “Modbus (TCP)”).
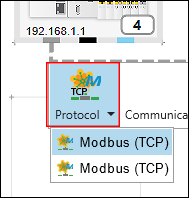
The selection options depend on the devices used.
Make the Device Settings on the “Settings” Panel
You can change the settings or parameters of the devices that have been added on the “Settings” panel. The panel is open by default. If it is not, open it using the context menu of the device and the [Settings] button.
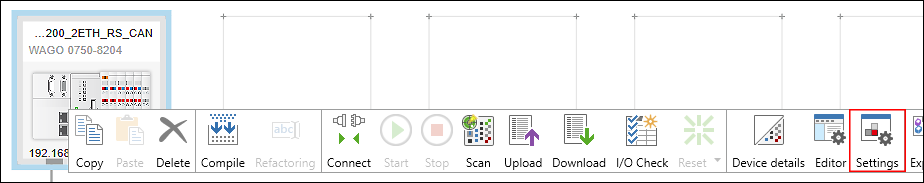
- Select the device in the network view.
- The tabs, entry screens and selection fields on the “Settings” panel depend on the specific device. The settings options displayed depend on the content of the particular device description file.
- Controller (Master):
Make all the general settings concerning the device, PLC and local bus on the first tabs. For example, you can modify the IP address.
Make Modbus settings on the “Modbus” tab. 
- Slave (Third-Party Device):
Third-party devices tend not to have any possible settings. If modifiable settings are displayed, then they are merely for communication with the controller, but they are not modified in the third-party device itself.
Program Application
- Select the controller.
- Open the “Program Structure” panel by clicking the [Program Structure] button on the “VIEW” tab of the menu ribbon.
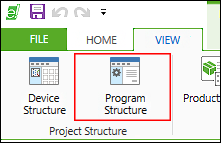
- Create your program (in the main “PLC_PRG” program or in a POU).
- Compile and validate your program on the “PROGRAM” tab with [Compile].
Configure Slave
For third-party devices, you can only used generic data points. You need these if you want to access existing data points, which can represent any position in the existing Modbus process image, in a certain way (using function codes), for example. The third-party device must provide the data points via the corresponding Modbus address so they can be further processed in the master.
You configure the slave in the data point configurator.
- To switch to the data point configurator, double-click the Device tile of the slave device.
- To create new generic data points, click [Add] in the context menu of “Generic Data Points.”
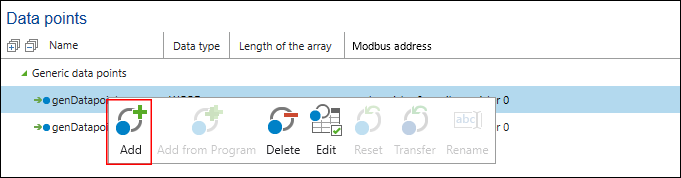
- If necessary, change the data type and Modbus address.
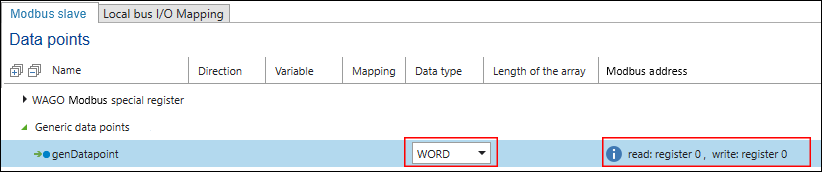
- In the context menu of the variable, click [Edit] and, if necessary, modify further settings, such as function code settings.
To take over existing data point configurations from third-party devices, you can import them via a CSV file and use this to integrate the third-party device into e!COCKPIT:
- Go back to the Network view.
- Select the slave and click the [Import] button on the “DEVICE” tab of the menu ribbon, “Advanced Device Functions” tab group.
- Select the corresponding CSV file.
- The data is displayed in the data point configurator.
Exporting data points to a CSV file is also possible. In this way, variables can be created or modified in batches outside of e!COCKPIT as well:
- Select the slave in the Network view and click the [Export] button on the “DEVICE” tab of the menu ribbon, “Advanced Device Functions” tab group.
- A CSV file is created.
- You can modify or add to the file using Microsoft Excel, for example.
- Then click [Import] and select the modified file.
- The data that has been created is displayed in the data point configurator.
Configure Connection between Master and Slaves
You can configure the connection between the master and slaves in the fieldbus configurator. Here you primarily make connection settings, display variables to transfer and create new variables.
- Click the Modbus connector of one of the two connected devices.
- Open the Modbus fieldbus configurator by clicking the [Configurator] button.
- The fieldbus configurator opens. The connection is shown in the header section of the configurator. If multiple slaves are connected to one master, you can modify the selection under “Selected Connection.”
- The fieldbus configurator is divided into two columns:
The left side shows the variables that are transferred from the slave to the master via the bus.
The right side shows the data points available on the slave. For a third-party device, these are merely generic data points. - In the right-hand column, select a slave data for the master to access.
Tip: You can select multiple data points by holding down the Control key. - Click [Map] in the context menu of the data point.
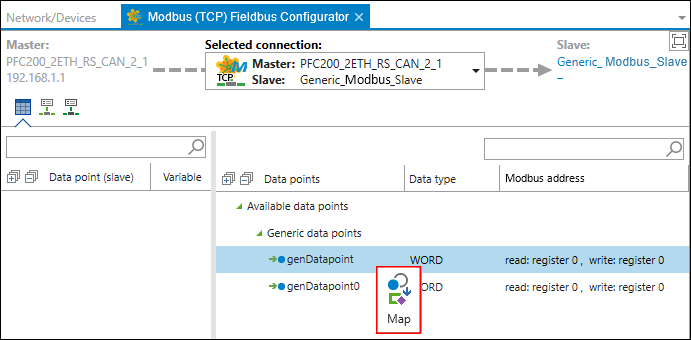
- The variable is generated in the master application. This establishes the connection to the slave data point.
- Change the cycle time (column T [ms]) to the required cycle time.
- You can now use the master variable in the master’s application.
Access Data Points
- Open the program structure and the main program of the master.
- In the master’s application, the variable is accessed as shown in the following figure.
- Tip: Press the [F2] key to open the input assistant for easy variable selection.
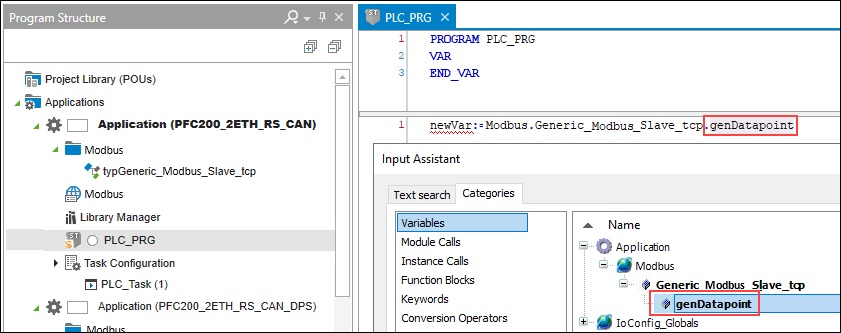
- In this way, a newly created slave data point has been made accessible via Modbus and read out in the master application.